The new ift guideline VE-15 "Multi-pane insulating glass - tested type statics according to DIN 18008" offers a legally secure and simple dimensioning of insulating glass according to DIN 18008 per diagram without the additional examination by a structural engineer.
Background: The "DIN 18008 - Glass in Construction" revised in 2020 has made glass dimensioning more precise, but also more complex. In the process, the simplification of verification for glass areas under 1.6 m² was also deleted without replacement.
From the point of view of building law, a static verification can therefore be required for every glazing. In order to make it possible for manufacturers of windows and insulating glass, as well as fabricators, dealers and installation companies, to dimension glass easily and in accordance with building regulations, ift Rosenheim, BF, BIV, VFF and TSD have developed a practical solution.
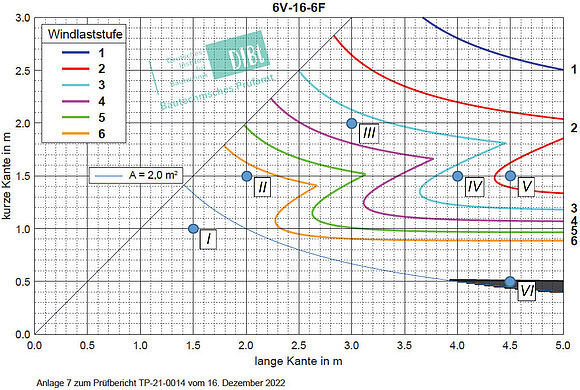
Together with Prof. Dr. Feldmeier (Rosenheim Technical University), dimensioning diagrams were calculated for 39 frequently used glass structures, which were tested and approved by DIBt.
If these design diagrams are used professionally, they can be used as type statics within the scope of the stated application conditions as proof under building law. No additional (test) structural engineer is required.
ift Rosenheim
Design of insulating glass - What do the legally relevant Eurocodes require?
An important technical and safety-relevant aspect of glass for windows, façades and entrance doors is mechanical safety, in particular the prevention of glass breakage as a result of wind and climate loads.
See also: Futuristic glass windows for impossible architecture in Austria
The introduction of the European Eurocode 1 "Actions on load-bearing structures - Parts 1-4" and the "DIN 18008 Glass in building - Design and construction rules - Parts 1 and 2" made glass design in Germany much more complex.
Likewise, the verification facilitation for glass areas less than 1.6 m² was deleted without replacement with the new DIN 18008-2:2020. This facilitation made it possible to dispense with the verification completely if certain marginal conditions were met.
From the point of view of brewing law, a corresponding structural analysis can therefore be required for every glazing. A calculation by various software programs without the necessary qualification for the preparation of stability proofs is not considered proof in the sense of building law, but rather a "preliminary design" that must be checked by a structural engineer.
Dimensioning made easy
In order to make it possible for manufacturers of windows and insulating glass, as well as for fabricators, dealers and installation companies, to dimension glass as proof of stability under building law, a type statics was created that has been tested and approved by the DIBt.
The project was initiated jointly by ift Rosenheim and the German trade associations Bundesverband Flachglas (BF), Bundesinnungsverband des Glaserhandwerks (BIV), Verband Fenster + Fassade (VFF) and Tischler Schreiner Deutschland (TSD). In cooperation with Prof. Dr. Franz Feldmeier, a diagram for 39 typical glass structures was developed, which enables a quick and easy "reading" of the permissible dimensions for various structures from the diagrams through the practice-oriented definition of boundary conditions (simplifications).
Also interesting: XXL insulating glass units: Weighing tons and still sensitive
In the course of this, adapted modification coefficients kmod were proposed and approved by DIBt for use in the verification procedure according to DIN 18008. With these "new" kmod values, the verification of small-format insulating glass is also possible, which otherwise would not be verifiable with the "old" kmod values due to too high climate loads.
Due to the testing of the German Institute for Building Technology (DIBt), the design diagrams (Annex 2 of the ift guideline) in connection with a correct determination of the wind load levels (Annex 1 of the ift guideline) can be used by the user as type statics.
Legal certainty
According to an opinion of the SMNG law firm for building law, the type test examined and recognised by the DIBt (see also § 66 Para. 4 Sentence 2 of the MBO) is regarded as structural proof that does not require any further examination. According to the VOB/C (see also the respective ATV), structural verifications are "special services" that are only part of the contractual services if they are specifically mentioned in the service description. These can be offered by the contractor and claimed accordingly. A corresponding claim for remuneration should therefore always be checked.













